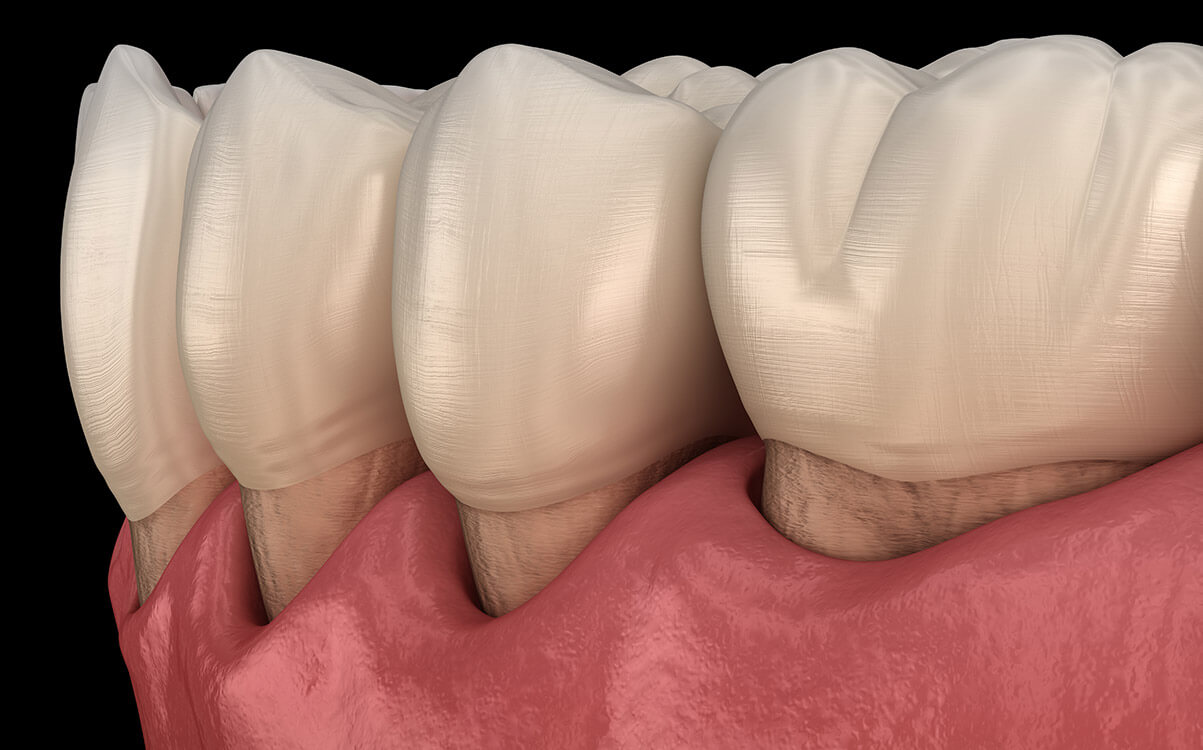
Receding Gums (Gum recessions) are familiar dental issues. Generally, gum recession takes place gradually; hence, many people may not know whether they have it or not. Sensitivity is usually the primary sign that you may be having this condition. In some instances, you might observe that your tooth seems elongated more than usual. Usually, you may feel the notch around your gum line.
It is important to note that gum recession is something that you should not ignore. Once you think or notice that you have gum recede, plan for an appointment with the dentist. There are available treatments that may repair your gums and avoid additional damage.
Table of Contents
What are Receding Gums?
Gum recession is a process where your gum margin surrounding your teeth pulls back or deteriorates. This exposes your tooth more or even your tooth’s root. Following gum recession, gaps or “pockets” develop between your gum line and teeth, forming a breeding ground for disease-causing bacteria.
What Happens If You Don’t Treat Gum Recession
If not treated, your teeth’ bone structure and the supporting tissue might be severely injured and can eventually cause tooth loss.
Receding Gums Causes
Typically, several factors might result to gum recession, which are:
Periodontal Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, refers to your gums’ inflammation and infection and other mouth structures. This swelling is a result of bacterial deposit accumulation, commonly known as plaque.
Some of the known gum recession causes that can contribute or result to gum disease include:
- Crooked teeth
- Use of tobacco product, including smoking
- Faulty or damaged fillings
- A genetic predisposition
- Prescriptions that might result to dry mouth
- Hormonal deviations because of oral contraceptives or pregnancy
- Certain immune disorders
- Partial dentures or bridges that are not fitting well
- Stress
- Poor oral hygiene
Below are two gum recession stages.
Gingivitis
During this stage, you may experience swelling, gum redness, and even gum bleeding. If gingivitis goes untreated, it can result in periodontitis.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is the second periodontal disease stage and might result in gum recession. As the connective tissues and gum shrinks from your tooth, a pocket will develop between the gum and your tooth, thus accumulating bacteria. With time, the accumulated bacteria will cause further swelling. If your gums recede a lot, it can cause bone loss, and it might loosen your teeth.
Incorrect or Forceful Brushing
Forceful teeth brushing can cause gum recession. Brushing your teeth will help you maintain healthy oral status. Nevertheless, an incorrect brushing practice might trigger gum recession. The gingival line is that part of your gum that connects with your teeth crown. Brushing too hard or incorrectly might harm the gingival margin, triggering gum recession and inflammation.
Some of the incorrect brushing elements that may cause gum recession include the following.
- Brushing your teeth in a horizontal, broad motion
- Applying a medium or hard-bristled toothbrush
- Using too much pressure
Clenching and Teeth Grinding
Some individuals grind their bottom and top teeth as they sleep. Over time the intense pressure caused by teeth grinding motion results in gum receding. Teeth clenching might also result in the loosening of your teeth from their sockets. Grinding creates some pockets between the gum and the tooth, where bacteria might build up. These bacteria cause swelling of the gum, which could cause a worse gum recession condition.
Injury
Supporting direct trauma to your gum tissue can result in receding of your gums in that part. Such injuries can happen in the situations outlined below.
- During an accident or a fall
- While wearing partial dentures
- During dental procedures
- While participating in contact sports
Receding Gums Symptoms
Listed below are some gum recession symptoms.
- Red, swollen gums
- Visibly lessening gums
- Pain around your gum line
- Exposed tooth roots
- Bleeding after flossing or brushing
- Loose teeth
- Bad breath
Receding Gums Diagnosis Process
Gum recession or any other form of gum condition are diagnosed by your dentist. Through some physical examination, the dentist can be able to identify some issues. They might also use a probe for measuring your gum pockets.
During this process, your dentist will use a small but painless ruler to get your gum pockets’ size. Typical pocket sizes should measure between one to three millimeters. When the size is beyond this range may be an indication of gum disease. Gum recession diagnosis might require a medical appointment with a dental specialist.
 Treatment
Treatment
Medications
A periodontist will prescribe the best mode of treatment in saving your teeth and gum tissues. To begin with, if your dentist finds an infection in your gums, they might prescribe some antibiotics. Additionally, other medications are used in treating the underlying elements that may lead to gum recession. They include the following.
- Antiseptic chips
- Topical antibiotic gel
- Enzyme suppressants
- Antimicrobial mouthwash
Surgery for Treating Receding Gums
Discussed below are some surgical processes used in gum recession treatment:
Root Planning and Open Fold Scaling
During this surgical procedure, your (gum doctor) periodontist or dentist will fold the affected gum and eliminate the damaging bacteria from your pockets. They later snugly secure your gum tissue in position over your tooth root; hence, removing the pockets or lessening their size.
Regeneration
When the bone that supports your teeth is destroyed due to gum recession, your dentist might suggest a procedure that can regenerate your lost tissue and bone. Like a pocket depth reduction procedure, your periodontist will fold your gum tissue back and eliminate the bacteria.
After which, a regenerative substance will be fixed, in return, will enable the body to regenerate tissue and bone. Some of the regenerative materials include a tissue-stimulating protein, graft tissue, or membrane. Your dentist will anchor your gum tissue over your teeth or tooth root after placing a regenerative material.
Soft Tissue Graft
Soft gum tissue graft procedures are several types; however, the commonly applied one is a connective tissue graft. During this procedure, a piece of your skin is chopped from the palate, and a subepithelial, connective tissue, is extracted and then sewed to your gum tissue within the exposed teeth root.
Another type of this surgery is known as free gingival graft. During this procedure, the tissue is directly taken from the mouth’s roof. Where the patient has adequate gum tissue around the affected teeth, your specialist will graft gum from the neighboring tooth instead of extracting the tissue from your palate. This refers to us as a pedicle graft. Your periodontist might suggest a suitable kind of procedure to choose depending on your specific needs.
Gum Recession Complications
It is estimated that gum diseases, including gum recession, are liable for approximately 70 percent loss of adult teeth. With less gum tissue to support tooth roots in position, your teeth might fall off. In some cases, multiple loose teeth are extracted by your dentist before they ever fall off. Generally, complex instances of receding gums need surgery to avoid additional damage.
Gum recession may lead to tooth loss. Therefore you may need treatment for missing tooth. The cost of dental implants is much more than the cost of treating your gum disease.
How to Prevent Receding Gums
Prevention
Listed below are valuable points that you may use to stop or to slow development receding gums.
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
For great oral hygiene, follow these tips.
- Choosing the shape and a size of your toothbrush that can allow you to access all parts of your mouth
- Use soft-bristled toothbrush in brushing your teeth twice in a day
- Flossing between your teeth once per day
- To flush out debris and reduce bacteria apply an antibacterial mouthwash
- Replace your toothbrushes after every two to four months
- Use fluoride toothpaste
- Regularly attending dental appointments
Correct Brushing Technique
Using the right brushing technique will help avoid bleeding and receding gums. The following guidelines might help you prevent plaque buildup on teeth and receding gums.
- Position your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle against the gums
- Applying gentle pressure, swing your toothbrush while using relative pressure back and forth with tight, small strokes.
- Brush the inner and outer surfaces, including the chewing tops, of your teeth.
- Hold your toothbrush vertically as you brush your front teeth’ inner surface.
- In total, the brushing should last for two minutes.
In managing your gum recede, you may also ask your dentist for some tips to modify the above technique.
Using Mouth Guard
Having a mouth guard as you sleep helps you avoid gum recession from teeth grinding. Using a mouth guard will function as a physical barrier by separating bottom teeth from the top teeth.
Replace the Ill-Fitting Dentures
With time, partial dentures might become unfit for your mouth. Generally, this is due to:
- Changes in jaw alignment
- Normal wear and tear of your partial dentures
- Gum ridges and the bone shrinking over time
Ill-fitting dentures may irritate and rub your gums, causing them to recede. You can avoid this by replacing them as required.
Regular Visits to Your Dentist
Regular dental inspections are necessary as they help detect early gum recession stages. Your dentist can identify and replace the ill-fitting or faulty partial dentures through checkups, which might cause gum recession.
Conclusion
A checkup for early gum recession stages is a wise idea. Are these questions still crossing your mind: How can I tell if my gums are receding? Do teeth fall out with receding gums? Get all answers to this and more when you contact Voss Dental for consultation. Be sure to visit us for more information about normal gums vs receding gums.